What is System Reserved Partition?
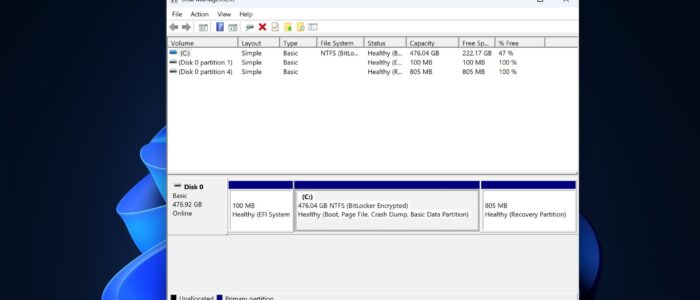
The System Reserved Partition is a small Partition that is automatically created during the Installation of the Windows Operation System, starting from Windows 7. It is a dedicated partition to store the Boot Manager, Boot Configuration data, and critical Bitlocker files. If you’re unsure whether to remove this partition, the answer is yes; doing so won’t affect your Windows operating system in any way. But it’s recommended not to delete it. Windows 10 and Windows 11 will automatically create a System Reserved partition When you install them on the clean disk. By default, Windows won’t allocate any drive letter for this partition, so you can’t see these partitions on Windows Explorer, the only way to see these partitions is to use Disk Management or a similar kind of Utility.
Typically System Reserved Partition size range from 100MB to 500 MB, depending on the Windows Version and how it was partitioned.
What is the Purpose of System Partition?
There are three important purposes for the System Reserved partition:
Boot Manager and Boot Configuration Data (BCD) Storage:
Once you start your computer, the Windows Boot Manager reads the Boot data from the Boot Configuration Data (BCD). BCD Contains the files necessary to boot Windows, such as the Boot Manager and Boot Configuration Data (BCD), During the system startup, the Boot Manager loads from this partition to initiate the operating system.
BitLocker Drive Encryption:
If your system is encrypted, the System Reserved Partition contains the files required for BitLocker to function before the main operating system is decrypted. The System Reserved partition is unencryped, when your computer boots the unencrypted System Reserved Partition loads first and then decrypts the main encrypted OS Drive and start the Windows Operation System. So the System Reserved partition is very important if you want to use a BitLocker encrypted drive, If your Operating system drive is encrypted then without the System Reserved Partition it won’t boot the OS drive, so deleting this drive is not recommended.
Recovery Options:
The System Reserved partition may store recovery tools and files which is very important for the Startup repair and System Recovery processes. Also, it has the necessary files to boot a Windows Recovery Environment or (WinRE), Learn more about WinRE or Windows Recovery Environment. WinRE contains troubleshooting features like System Restore, System Image Recovery, Automatic Repair, and access to the command prompt, these features are very much important to troubleshoot the OS booting issues when your System OS is corrupted or missing boot files, damaged system files or any other issues. During the System Recovery, the system may redirect the boot process to the System Recovery Environment, to load these recovery tools to attempt the repair to fix the booting issues before the OS drive starts. That’s why these tools are isolated and hidden in a dedicated partition. Deleting this partition or corruption to the System Reserved partition will leave the users to rely on External recovery methods, such as booting from installation media.
When Windows will create the System Reserved Partition?
When installing the Windows Operating system on a new, unpartitioned drive, Windows will automatically create the System Reserved Partition during the clean installation. The Windows Installer creates a small partition, typically 100 MB to 500 MB, to store the essential boot files, the Boot Manager, Boot Configuration Data (BCD), and recovery tools. This partition will be created if the drive is blank or if you choose Windows to handle the Partitioning process. However, if you manually partition the drive before the installation or if you install the Windows in an existing partition, the system-reserved partition will not be created.
Is Deleting System Reserved Partition Safe?
Deleting System Reserved Partitions is not recommended. Unless you know exactly what you are doing and have taken the necessary precautions. Here are the following reasons Why you should not Delete System Reserved Partition:
Risks of boot failure:
The partition contains the necessary boot files. Deleting it will prevent the system from booting. Causes “Missing Boot Configuration” error
BitLocker incompatibility: If BitLocker is enabled, deleting this partition can cause encryption problems or make the encrypted drive inaccessible.
Latest problems: Some update and recovery processes rely on this partitioning. Removing it may interfere with these operations.
When can you delete System Reserved Partition?
You may consider deleting the System Reserved Partition in the following situations:
Before installing Windows: During a Windows reinstallation, you can avoid creating this partition by formatting the drive and installing the operating system on a single primary partition.
After installation (with caution): Move the boot files to the main partition before deleting. This requires using a tool like bcdboot or editing the boot configuration via Command Prompt.
How to Prevent the System Reserved Partition from Being Created?
If you don’t want this partition for whatever reason, then the ideal thing is to prevent it from being created in the first place. Instead, allow Windows Installer to create partitions in unallocated space. You can use a separate disk partitioning tool to create a single partition that uses all of the unallocated space before running Windows Installer… When installing Windows, simply select the partition you created. Because there is no location for the System Reserved partition, the installer places the boot files directly on your main system partition.
Note that this does not save the total space used by the System Reserved partition (generally 100 MB, 350 MB, or 500 MB), because those boot files are still needed – they will be stored. Only on your main partition… To achieve this goal You’ll need to use a disk partitioning tool other than the Windows installer’s graphical tool, or you can follow these steps to manage this process directly within the Windows installer.
Open Command Prompt: During the Windows installation process, press Shift + F10 to open a Command Prompt window.
Run DiskPart: Type diskpart and press Enter to open the disk partitioning tool.
Create a partition: Use DiskPart to create a new partition in unallocated space. For example, if you have only one empty drive. Type the following command. Select Disk 0 to select the first disk, and type Create partition primary to Prioritize partitions to create partitions using all unallocated space.
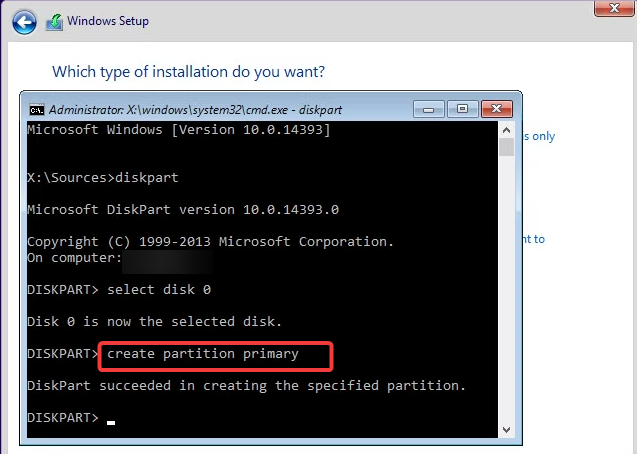
Continue Installation: Continue the Windows installation when prompted to select a partition. Select the partition you created. Follow these steps, and Windows will install on a single partition without creating a System Reserved partition.
Read Also:
Fix We couldn’t update system reserved partition error while installing Windows 11
How to Check Disk Partition Style, GPT, or MBR Partition?