Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a protocol for mapping an Internet Protocol address (IP address) to a physical machine address that is recognized in the local network. For example, in IP Version 4, the most common level of IP in use today is 32 bits long address. In an Ethernet local area network, however, addresses for attached devices are 48 bits long. (The physical machine address is also known as a Media Access Control or MAC address.) mapping between IP addresses and MAC addresses on a network is usually called the ARP cache, which is used to maintain a correlation between each MAC address and its corresponding IP address. ARP provides the protocol rules for making this correlation and providing address conversion in both directions.
How ARP Cache Works?
When a device sends a message to a device with a particular IP address, it first checks its ARP Cache table to see if the IP address is mapped to the MAC address. If the mapping exists, the device can use the MAC address in the cache to transmit the message. If a mapping doesn’t exist, the device sends out the ARP request to the network asking for the MAC address associated with the IP address. ARP cache stores the new results in the table for future reference. These cache entries have a limited lifetime and are removed from the cache after a certain period of time, or if the cache becomes full and new entries need to be added.
Benefits of Clearing ARP Cache:
If you are a network administrator, then you must know how to clear the ARP cache, clearing the ARP cache will help you to troubleshoot Network related issues.
Resolving network connectivity issues: In some cases, clearing the ARP cache can help resolve network connectivity issues. If the cache contains outdated or incorrect mappings, it can cause problems with network communication. By clearing the cache, the device can rebuild its mapping table with accurate and up-to-date information.
Security: In some cases, attackers can manipulate the ARP cache to launch an attack, such as ARP spoofing. Clearing the ARP cache can help prevent such attacks by removing any potentially malicious entries.
Troubleshooting: When troubleshooting network issues, clearing the ARP cache can help diagnose problems with network connectivity. It can help determine if the issue is related to outdated or incorrect mappings in the cache.
This article will guide you to Clear ARP Cache using Command prompt in Windows 11.
Clear ARP Cache using Command prompt in Windows 11:
Before clearing the ARP Cache, first, you need to display the list of ARP entries, here are the steps for viewing the ARP table.
Open the Command prompt in elevated mode, click on the start menu and search for Command Prompt and right click on it and choose Run as Administrator.
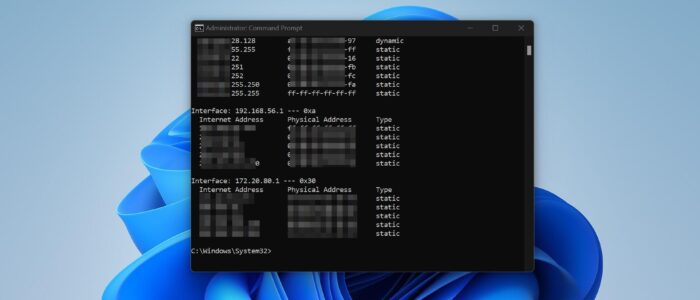
Type the following command to display the ARP Cache.
arp -a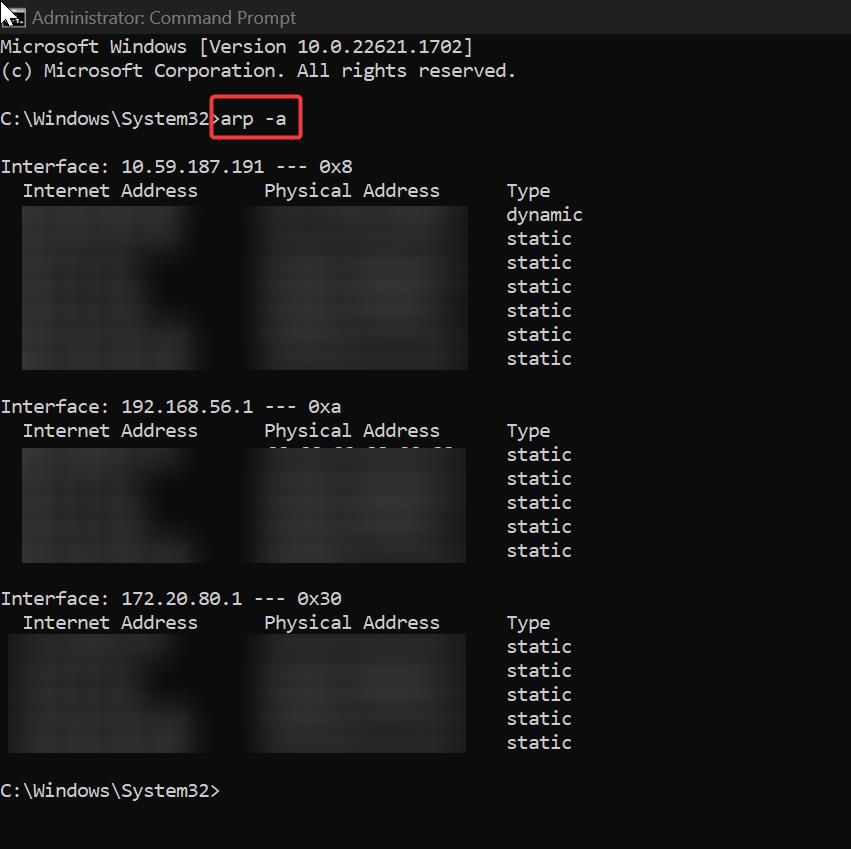
Once you verified the ARP entries, type the following command to clear the ARP cache.
netsh interface ip delete arpcacheOnce you executed the command, close the Command Prompt and restart your system once.
Again, type arp -a command to verify the ARP cache.
Read Also:
Find MAC address using arp command inside LAN?
How to Create Batch file to fix Network issues in Windows 10?