Safe mode is a diagnostic mode of a computer operating system (OS). It can also refer to a mode of operation by application software. In Windows, safe mode only allows essential system programs and services to start up at boot. Safe mode is intended to help you to fix most of the problems within an operating system. In safe mode, an operating system has reduced functionality, but the task of isolating problems is easier since many non-core components are disabled, such as sound, network drivers, graphics drivers, etc. It varies by the operating system. From Windows NT to Windows 7 you can access the safe mode by pressing F8. But this traditional F8 for safe mode option was canceled by Microsoft. This traditional method was changed in Windows 8,8.1 and 10 to reduce the boot time process. Either Shift-F8 or a special GUI-based workaround is necessary to access safe mode. In this post, we’ll see how to Boot into Safe Mode Using Command Prompt.
Boot into Safe Mode Using Command Prompt:
First, Open Command Prompt in elevated mode and enter the following command and hit enter.
shutdown.exe /r /o
Once you enter this command, the system will restart in less than one minute and boot into recovery mode.
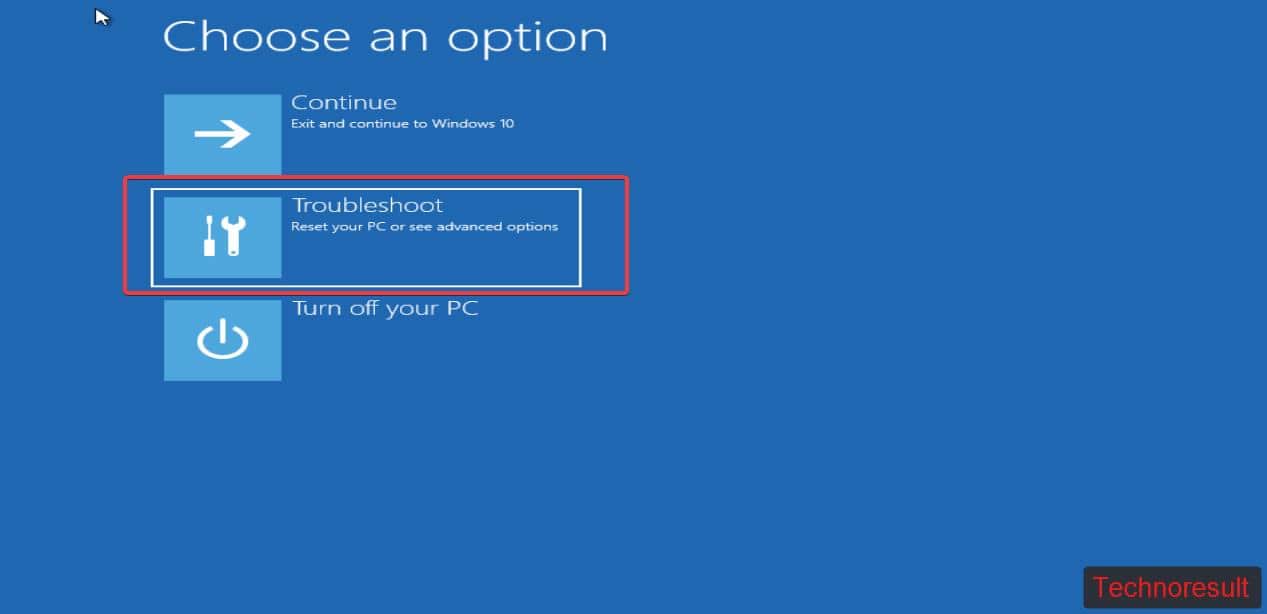
Next, When the computer restarts, it will show the “Choose an Option” section, here select the Troubleshoot option from the list.
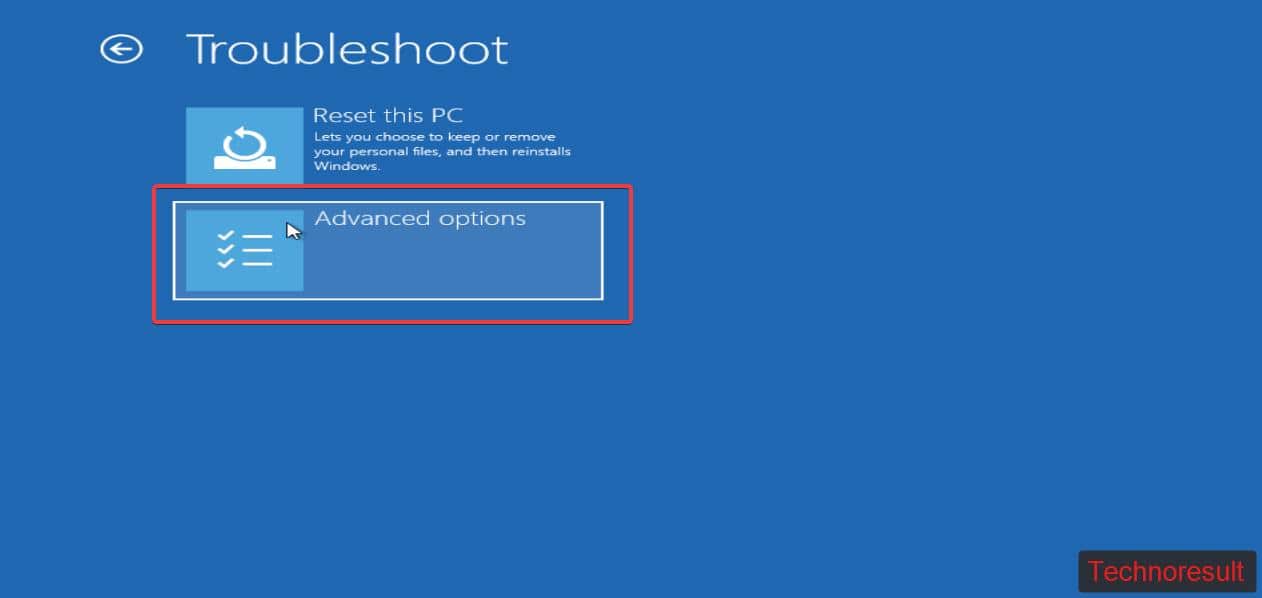
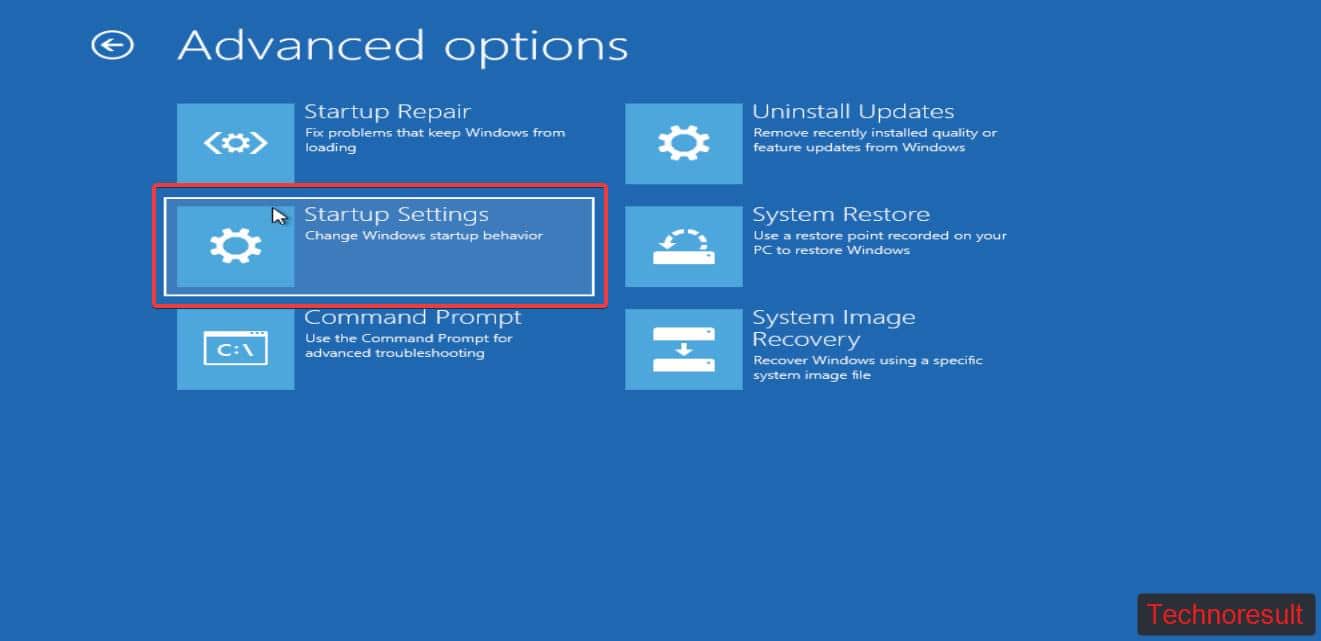
Next click on Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart.
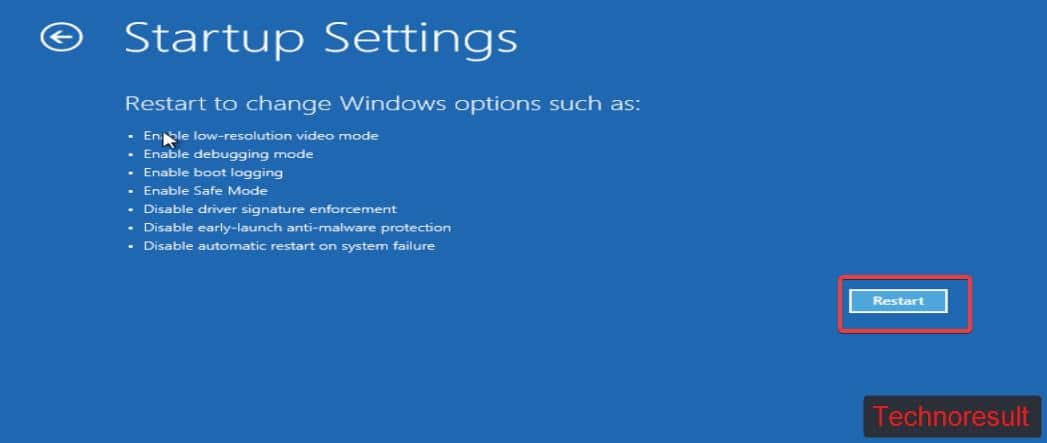
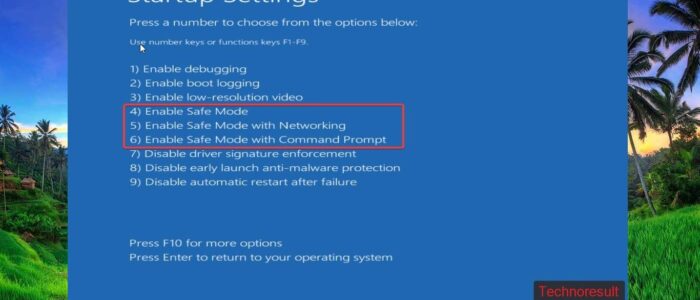
Now the system will restart and give you option to load safe mode, press the following keyboard buttons to enter into safe mode.
Press F4 or 4 to Enter Safe Mode
Press F5 or 5 to Enable Safe Mode with Networking
Press F6 or 6 to Enable Safe Mode with Command Prompt.
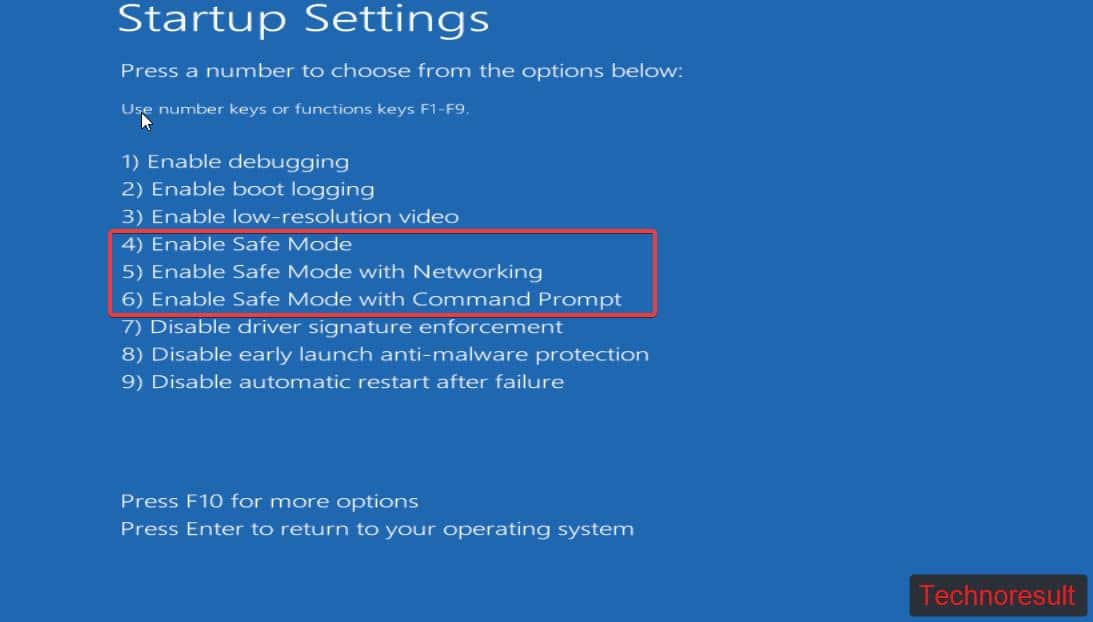
Once you Press on these buttons, your computer will restart and boot into safe mode.
Read Also:
How to Disable Safe Mode in Windows 11?