In Windows 10 Group Policy is a feature that controls the working environment of user accounts and computer accounts. Group Policy provides centralized management and configuration of the operating system, user’s settings, applications, in an Active Directory environment. A set or collection of Group Policies is called Group Policy Object. A Version of Group Policy is called as a Local Group Policy (LGPO). Local GPO allows managing Group Policy without Active Directory on Standalone Computers. We all know group policies are used to control what users can and cannot do on a computer system. For example, a Group Policy can be used to enforce a password complexity policy that prevents users from choosing an overly simple password. Other examples include allowing or preventing unidentified users from remote computers to connect to a network share or to block/restrict access to certain folders. Each time you set or configure a policy you need to update the Group Policy. This article will guide you to Update Group Policy in Windows 10.
Update Group Policy:
In Windows, if you want to Update Group Policy then you have to use the Windows built-in command-line tool called GPUPDATE.exe. Gpupdate command refreshes a computer Local Group Policy and any Active Directory-based Group Polices. This command is available in almost all the versions of Microsoft Operating Systems.
Syntax of Gpupdate command:
Description: Updates multiple Group Policy settings.
Syntax: Gpupdate [/Target:{Computer | User}] [/Force] [/Wait:] [/Logoff] [/Boot] [/Sync]
Parameters:
| /Target:{Computer | User} | Specifies that only user or only computer policy settings be refreshed. By default, both user and computer policy settings are refreshed. |
| /Force | Reapplies all policy settings. By default, only policy settings that have changed are applied. |
| /Wait:{value} | Sets the number of seconds to wait for policy processing to finish. The default is 600 seconds. The value ‘0’ means not to wait. The value ‘-1’ means to wait indefinitely. When the time limit is exceeded, the command prompt returns, but policy processing continues. |
| /Logoff | Causes a logoff after the Group Policy settings are refreshed, which is required for those client-side extensions that don’t process policy on a background refresh cycle but do during log on. Examples include user-targeted Software Installation and Folder Redirection. This option has no effect if there are no extensions called that require a logoff. |
| /Boot | Causes a reboot after the Group Policy settings are refreshed, for those client-side extensions that don’t process policy on a background refresh cycle but do at startup. Examples include computer-targeted Software Installation. This option has no effect if there are no extensions called that require a reboot. |
| /Sync | Causes the next foreground policy application to be done synchronously. Foreground policy applications occur at computer boot and user login. You can specify this for the user, computer or both using the /Target parameter. The /Force and /Wait parameters are ignored if specified. |
How to Update Local Group Policy?
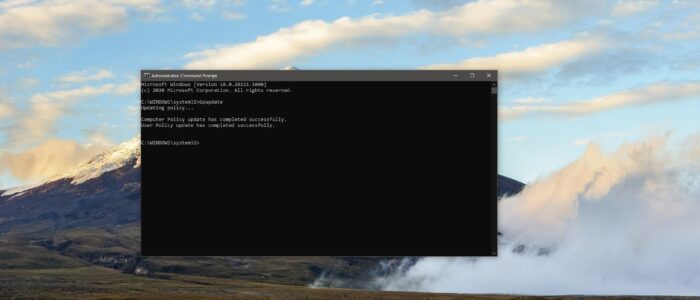
Open Command Prompt in elevated mode and type the following commands.
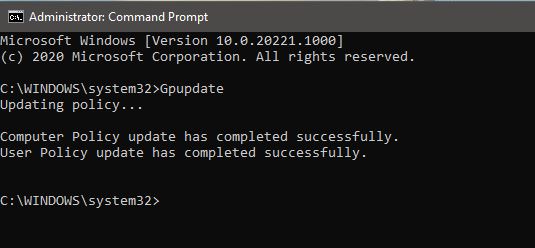
Gpupdate
This command will force update only the changed policies.
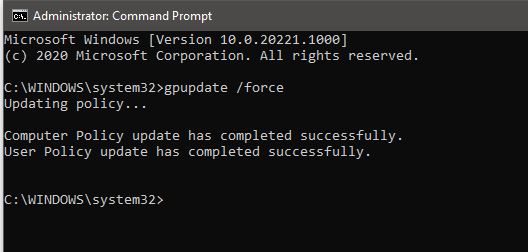
Gpupdate /force This command will force an update or refresh all policies.
After the Policy update, you will get the successful message. The computer Policy update has completed successfully. The user Policy update has completed successfully.