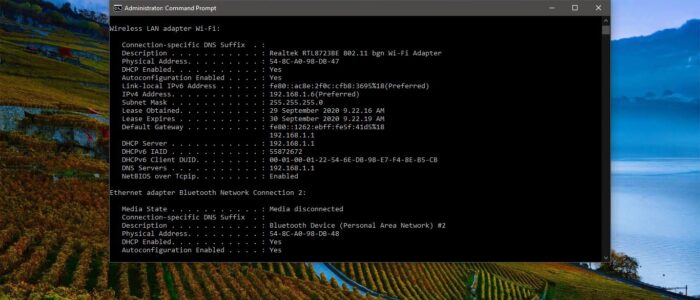
One of the most important things that must be completed when troubleshooting a networking issue is to find out the specific IP configuration of the variously affected hosts. The utilities that can be used to find out this IP configuration information include the IPconfig utility on Windows machines. Displays all current TCP/IP network configuration values and refreshes Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS) settings. Used without parameters, IPconfig displays the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway for all adaptors. In this article will discuss about ipconfig, ipconfig /all, ipconfig /Release, ipconfig /Renew and to check ipconfig in Windows.
How to check ipconfig in windows?
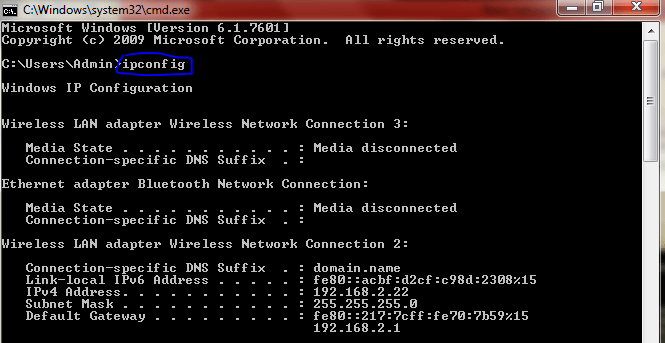
Open Run command by Pressing Windows + R and type Cmd and hit enter this will open the Command Prompt. Now Type ipconfig in the command prompt, This command will display the current internet protocol information.
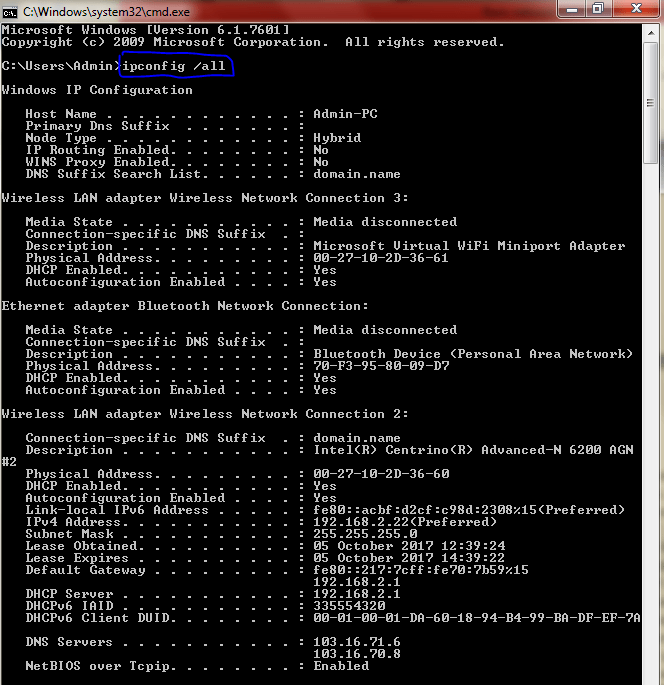
check ipconfig /all:
Displays the full TCP/IP configuration for all adaptors. Without this parameter, ipconfig displays only the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway values for each adaptor. Adaptors can represent physical interfaces, such as installed network adaptors, or logical interfaces, such as dial-up connections.
check ipconfig /Renew:
Renews DHCP configuration for all adaptors (if an adaptor is not specified) or for a specific adaptor if the Adaptor parameter is included. This parameter is available only on computers with adaptors that are configured to obtain an IP address automatically. To specify an adaptor name, type the adaptor name that appears when you use ipconfig without parameters.
Ipconfig /release:
Sends a DHCPRELEASE message to the DHCP server to release the current DHCP configuration and discard the IP address configuration for either all adapters (if an adapter is not specified) or for a specific adapter if the Adapter parameter is included. This parameter disables TCP/IP for adapters configured to obtain an IP address automatically. To specify an adapter name, type the adapter name that appears when you use ipconfig without parameters.
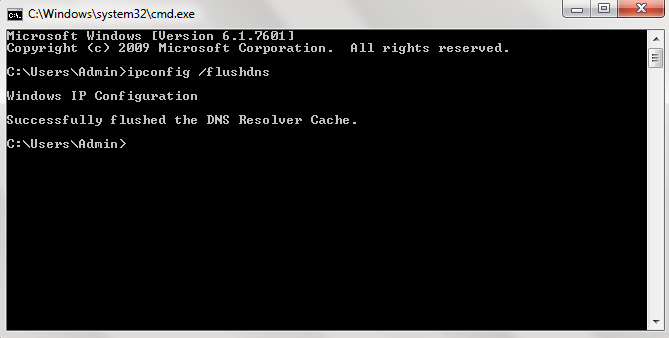
Ipconfig /flushdns:
Flushes and resets the contents of the DNS client resolver cache. During DNS troubleshooting, you can use this procedure to discard negative cache entries from the cache, as well as any other entries that have been added dynamically.
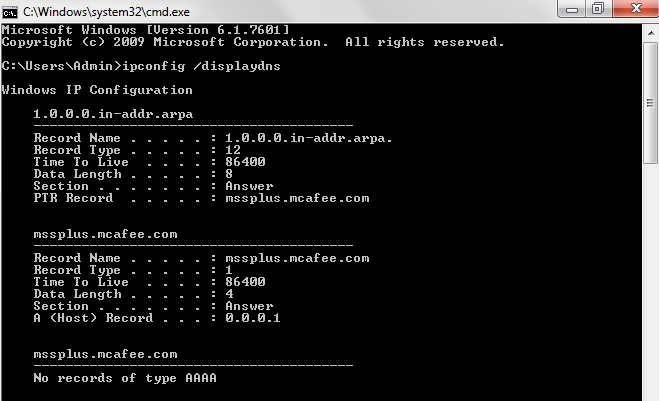
Ipconfig /displaydns:
Displays the contents of the DNS client resolver cache, which includes both entries reloaded from the local Hosts file and any recently obtained resource records for name queries resolved by the computer. The DNS Client service uses this information to resolve frequently queried names quickly, before querying its configured DNS servers.
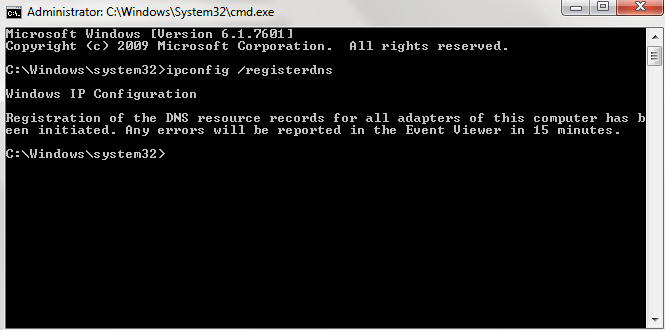
Ipconfig /registerdns:
Initiates manual dynamic registration for the DNS names and IP addresses that are configured at a computer. You can use this parameter to troubleshoot a failed DNS name registration or resolve a dynamic update problem between a client and the DNS server without rebooting the client computer. The DNS settings in the advanced properties of the TCP/IP protocol determine which names are registered in DNS.